Home » Geotechnical Services
Geotechnical Services
Geotechnical Investigations
Geotechnical soils investigations involve assessing the physical, mechanical, and chemical properties of soil and rock at a construction site. This process is essential for designing safe and stable foundations and understanding site conditions.
Geotechnical investigations are a critical first step in ensuring the safety, stability, and success of construction projects.
Key aspects include:
Purpose
- Determine soil bearing capacity and suitability for construction.
- Identify potential hazards like liquefaction, settlement, or slope instability.
- Provide data for foundation design, earthworks, and retaining structures.
Key Activities
- Site Exploration: Drilling boreholes, digging test pits, and performing in-situ tests (e.g., SPT, CPT).
- Sampling: Collecting disturbed and undisturbed soil samples for laboratory analysis.
- Testing: Conducting tests for strength, compressibility, permeability, and chemical composition.
Benefits
- Reduces construction risks by identifying soil-related issues early.
- Ensures cost-effective and reliable foundation design.
- Helps comply with regulatory and safety standards. Geotechnical investigations are a critical first step in ensuring the safety, stability, and success of construction projects.
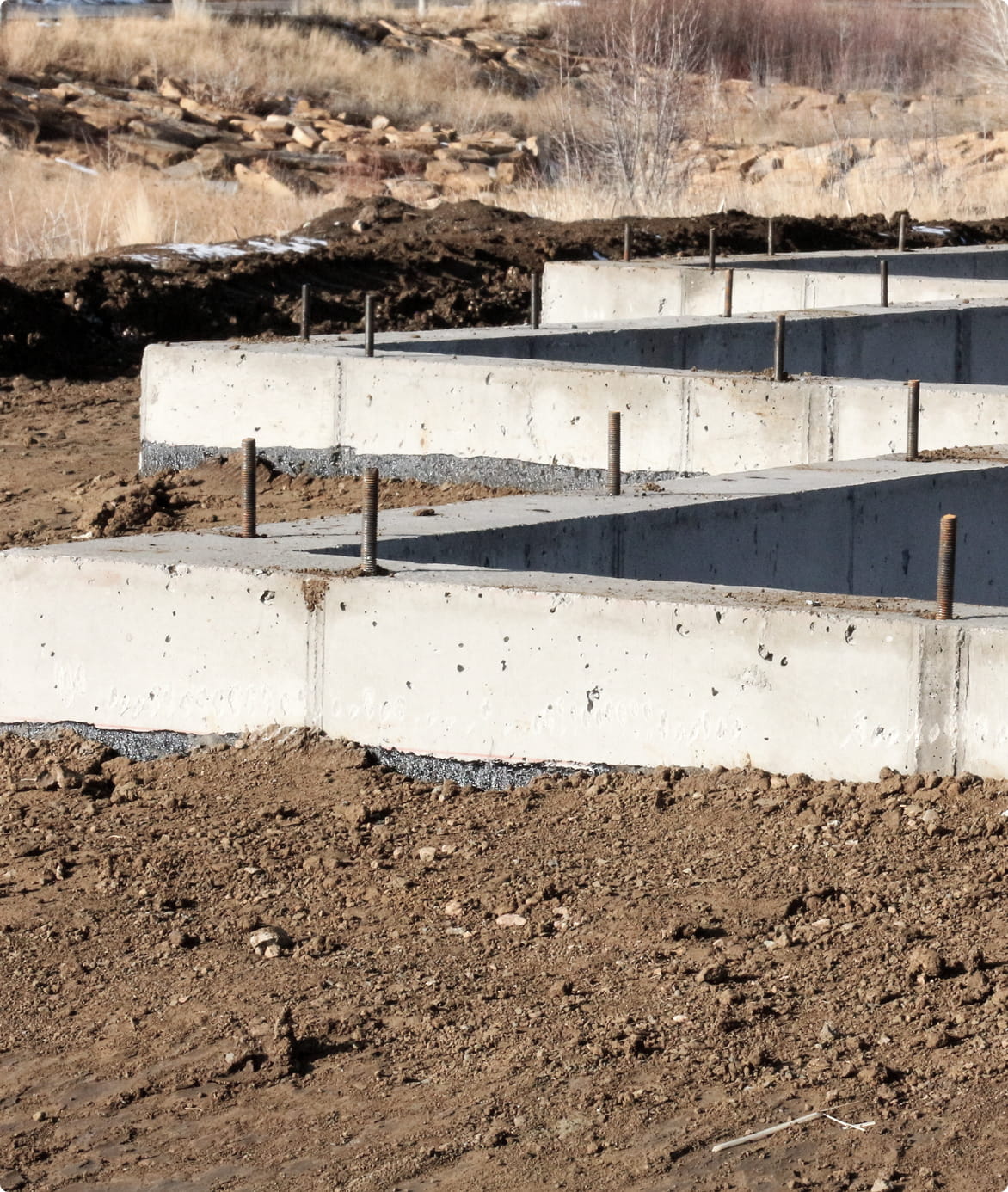
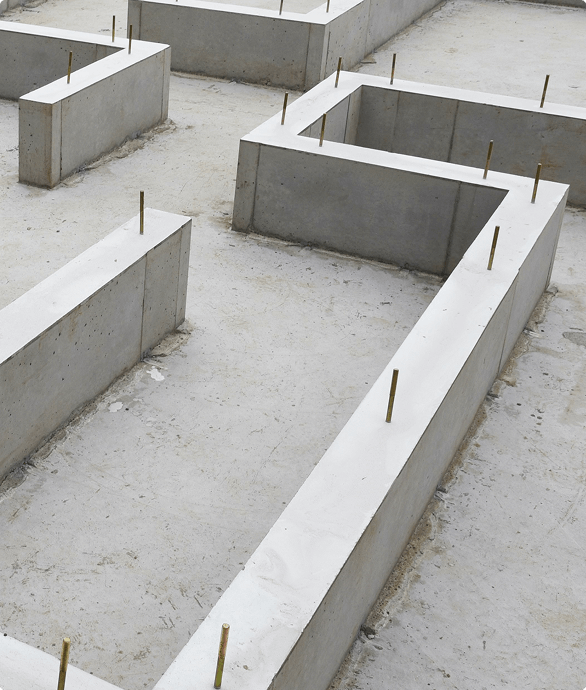


Foundation Design
Foundation design involves creating structural systems that safely transfer building loads to the ground, ensuring stability and durability. It accounts for soil conditions, building loads, and environmental factors.
Key aspects include:
Purpose
- Distribute structural loads evenly to prevent settlement or failure.
- Provide stability against lateral forces (e.g., wind or seismic activity).
- Ensure long-term performance and safety of the structure.
Types of Foundations
- Shallow Foundations: Spread footings, mat foundations, or slab-on-grade for light to moderate loads.
- Deep Foundations: Piles or drilled shafts for heavy loads or weak soils.
Design Considerations
- Geotechnical Analysis: Soil bearing capacity, settlement, and groundwater conditions.
- Structural Loads: Dead, live, wind, and seismic loads.
- Environmental Factors: Frost depth, erosion, and drainage.
Benefits
- Ensures structural safety and stability.
- Prevents differential settlement and structural damage.
- Optimizes construction costs through tailored solutions.
Slope Stability Analysis
Slope stability analysis evaluates the safety and stability of natural or engineered slopes to prevent failure. It identifies potential risks, determines factors of safety, and guides the design of stabilizing measures.
Slope stability analysis is critical for managing risks and ensuring safe development in areas with sloped terrain.
Key aspects include:
Purpose
- Assess the risk of slope failure under various conditions.
- Design safe slopes for construction, mining, or infrastructure projects.
- Mitigate hazards like landslides or erosion.
Methods
- Analytical Methods: Limit equilibrium methods (e.g., Bishop’s or Janbu’s methods) to calculate factors of safety.
- Numerical Methods: Finite element analysis for complex conditions.
- Empirical Approaches: Based on field observations and past performance.
Key Factors
- Geotechnical Properties: Soil strength, cohesion, and friction angle.
- Hydrology: Groundwater levels and seepage pressures.
- Loads and Geometry: Slope angle, height, and external forces (e.g., seismic or construction loads).
Stabilization Solutions
- Retaining structures, soil nails, or anchors.
- Drainage systems to manage water pressure.
- Grading or vegetation to reduce erosion.
Benefits
- Ensures safety and reduces risks to structures, infrastructure, and human lives.
- Guides efficient and cost-effective slope design.
- Complies with regulatory standards and mitigates environmental impacts.
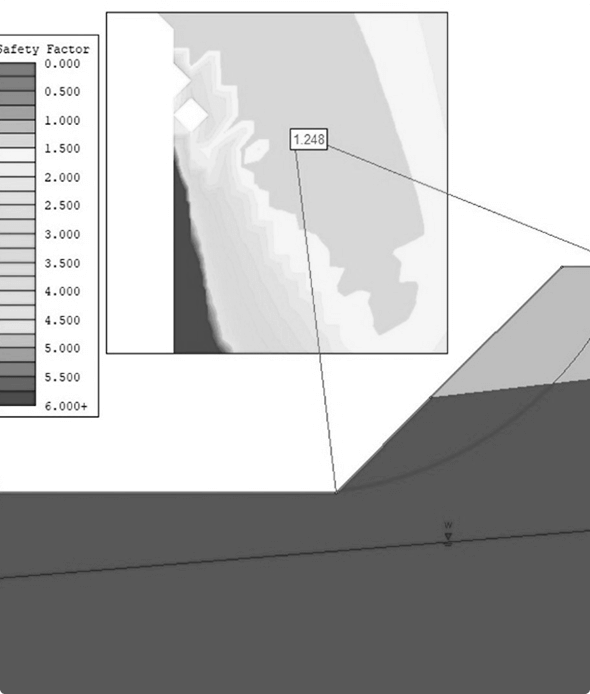

Working Platform Design & Certification
Working platform design involves creating temporary, stable surfaces to support heavy construction equipment, such as cranes and piling rigs, during site operations. It ensures safety and operational efficiency in challenging ground conditions.
Working platform design is an essential component of construction planning, particularly in projects involving heavy machinery on soft or unstable ground.
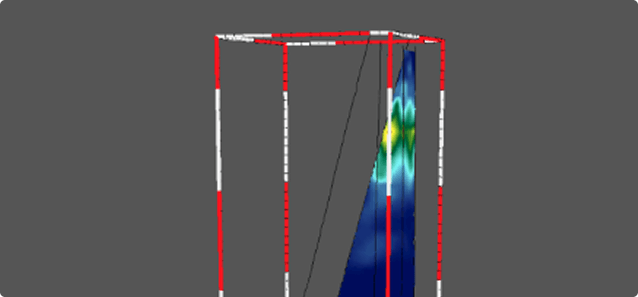
Cross Hole Seismic Testing
Seismic tomography provides high-resolution 2D or 3D images of seismic velocities between boreholes. The method is used to delineate geological structures, to map cavities and weak zones and to specify mechanical soil and rock properties. Geophysicists and engineers apply this method to investigate the foundation and underlying rock of buildings and bridges in order to characterize the subsurface before infrastructure is built and to image time-dependent processes.


